Icd10cm Code For Acute Peritonitis
The ICD code K65 is used to code Peritonitis. Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of the abdominal organs. Peritonitis may be localized or generalized, and may result from infection (often due to rupture of a hollow abdominal organ as may occur in abdominal.

Peritonitis 10 Symptoms of Peritonitis
K65.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM K65.0 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K65.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 K65.0 may differ. Applicable To.

Icd 10 Code For Perforation Peritonitis
Peritonitis. K65 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM K65 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K65 - other international versions of ICD-10 K65 may differ.

Peritonitis Generalisata PDF
Introduction. Peritonitis, an inflammation of the peritoneum, is a life-threatening acute surgical emergency. It presents with severe abdominal pain and is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality ranging from 10%-60% in surgical settings [].Existing literature shows that etiologies of peritonitis vary by geographic locations and local environmental factors with genetic predisposition.

ISPD Peritonitis Update 2022 — NephJC
Diseases of peritoneum and retroperitoneum. ( K65-K68) Peritonitis. ( K65) K65.0 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of generalized (acute) peritonitis. The code is valid during the current fiscal year for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions from October 01, 2023 through September 30, 2024.

Peritonitis Generalisata PDF
The abdomen is the second most common source of sepsis and secondary peritonitis. [ 1] Intra-abdominal sepsis is an inflammation of the peritoneum caused by pathogenic microorganisms and their products. [ 2] The inflammatory process may be localized (abscess) or diffuse in nature. (See Pathophysiology .) Peritonitis is most often caused by.

Peritonitis Nursing Care Management and Study Guide
Peritonitis. Peritonitis is inflammation in your peritoneum, the tissue that lines the inside of your abdominal cavity. It's usually caused by an infection, and sometimes by irritating bodily fluids. Infection in your peritoneum is especially dangerous because it can affect your abdominal organs. It can also transfer to your bloodstream and.

Peritonitis Generalisata PDF
The importance of the extent of peritonitis is highlighted in a prospective study of 92 patients with secondary peritonitis proven on laparotomy. 12 Patients with four quadrant peritonitis at the time of surgery had a mortality rate of 36% compared with an average in-hospital mortality of 19% in all patients (P=0.003). 12 The presence of fecal.

Peritonitis Med Surg Mnemonics & More Medical surgical nursing, Surgical nursing, Nursing
The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM K35.2 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K35.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 K35.2 may differ. The following code (s) above K35.2 contain annotation back-references that may be applicable to K35.2 : K00-K95. 2024 ICD-10-CM Range K00-K95.

Peritonitis What is it, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More Osmosis
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes. K65.0 - Generalized (acute) peritonitis. The above description is abbreviated. This code description may also have Includes, Excludes, Notes, Guidelines, Examples and other information. Access to this feature is available in the following products: Find-A-Code Essentials. HCC Plus.
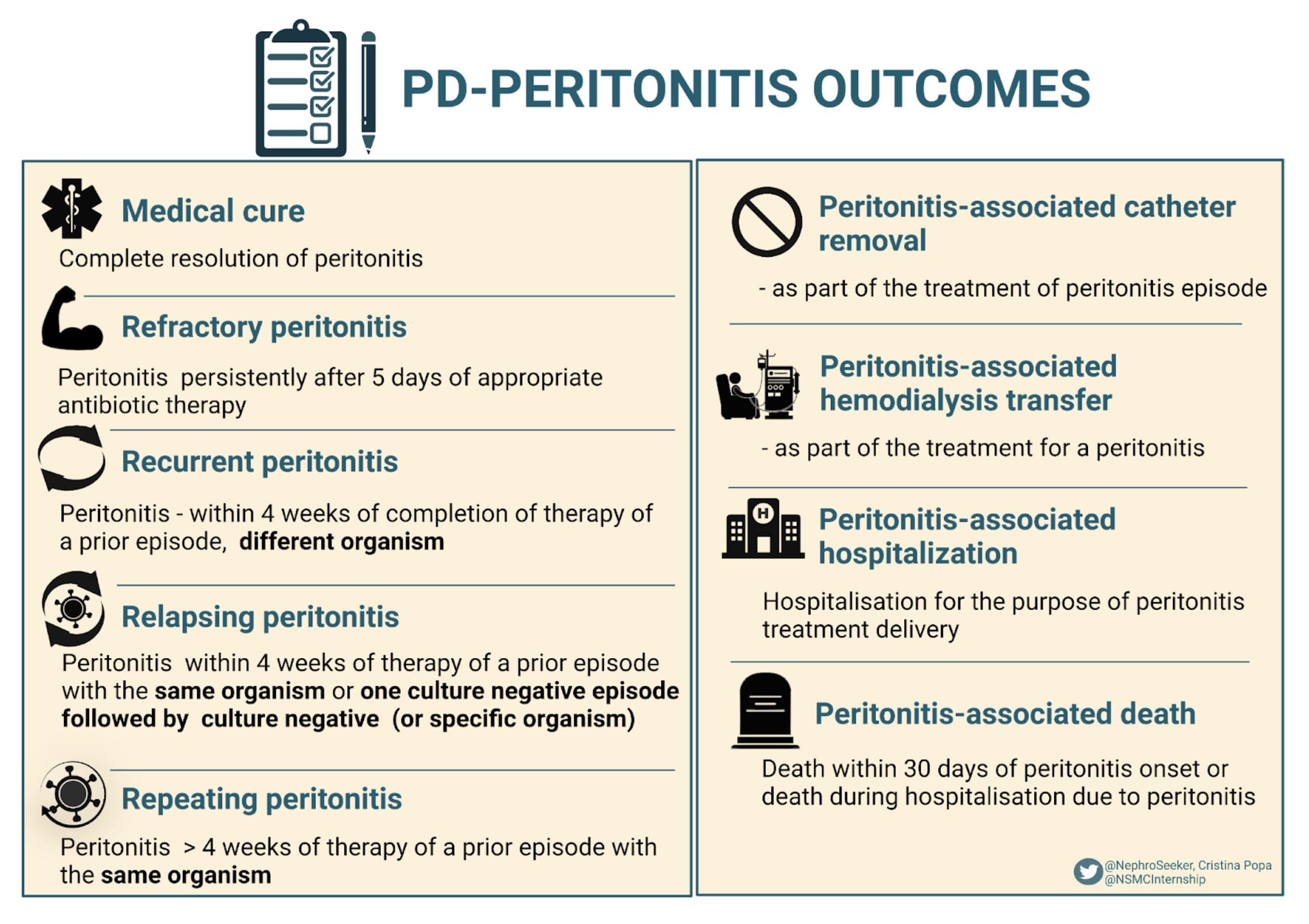
ISPD Peritonitis Update 2022 — NephJC
Other peritonitis. K65.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM K65.8 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K65.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 K65.8 may differ.

(PPTX) Peritonitis Generalisata DOKUMEN.TIPS
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is a term used to describe acute infection of ascites, an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdomen without a distinct or identifiable source of infection.[1][2] SBP virtually always occurs in patients with cirrhosis and ascites and is suspected when the patients present with abdominal pain, fever, or altered mental status.

Peritonitis Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Peritonitis usually happens due to an infection from bacteria or fungi. There are two types of peritonitis: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. This infection is caused by bacteria. It can happen when someone has liver disease, such as cirrhosis, or kidney disease. Secondary peritonitis.

Peritonitis Generalisata PDF
K65.0. Generalized (acute) peritonitis Billable Code. K65.0 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Generalized (acute) peritonitis . It is found in the 2024 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2023 - Sep 30, 2024 . ↓ See below for any exclusions, inclusions or.
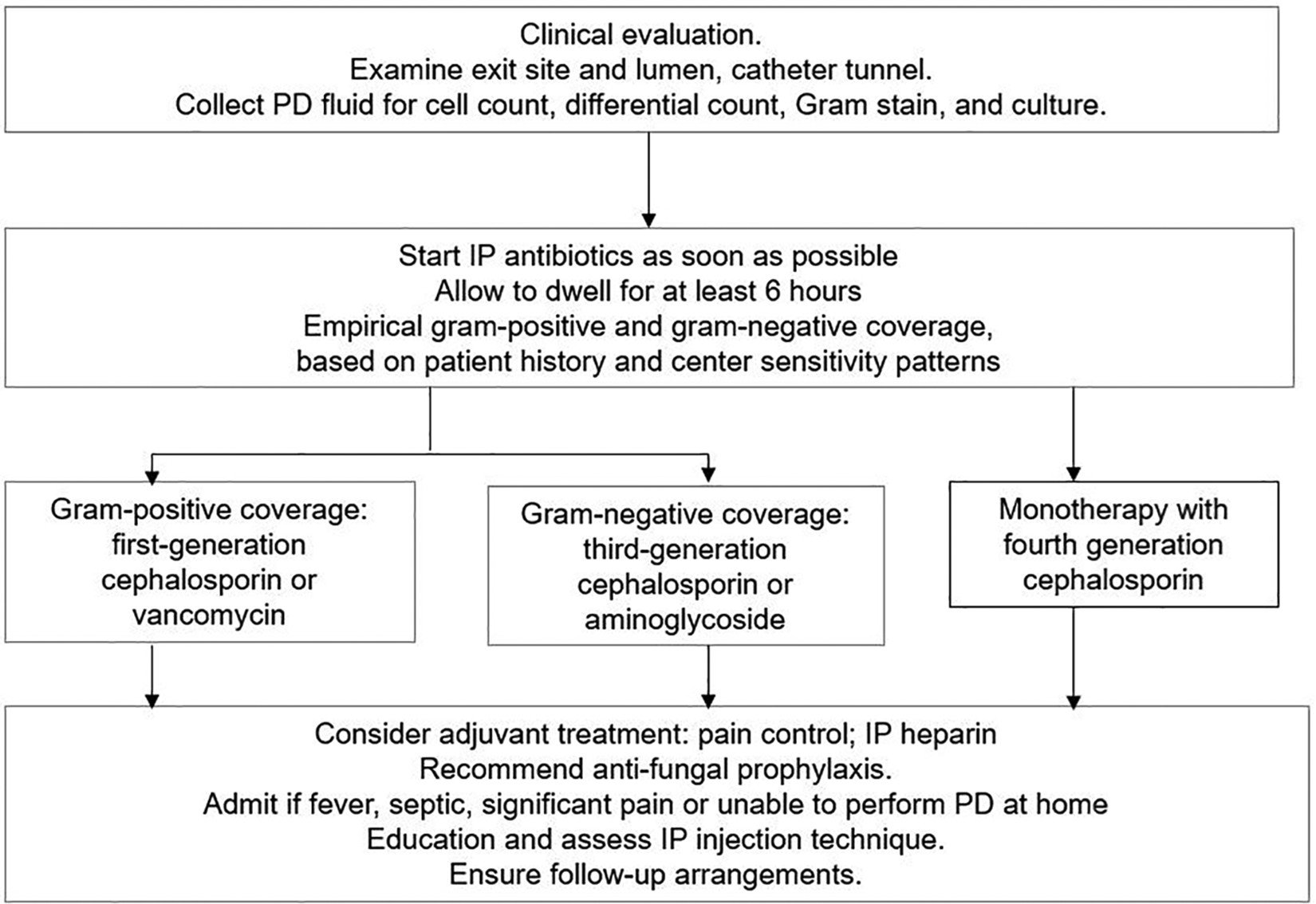
ISPD Peritonitis Update 2022 — NephJC
Peritonitis is a serious and potentially fatal inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. This article from PubMed Central (PMC) reviews the epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of peritonitis, with a focus on the role of the microbiome and the immune system. It also discusses the challenges and future directions for research and clinical.

ISPD Peritonitis Update 2022 — NephJC
Peritonitis, unspecified. K65.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM K65.9 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K65.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 K65.9 may differ.