
Stages Of Meiosis 2
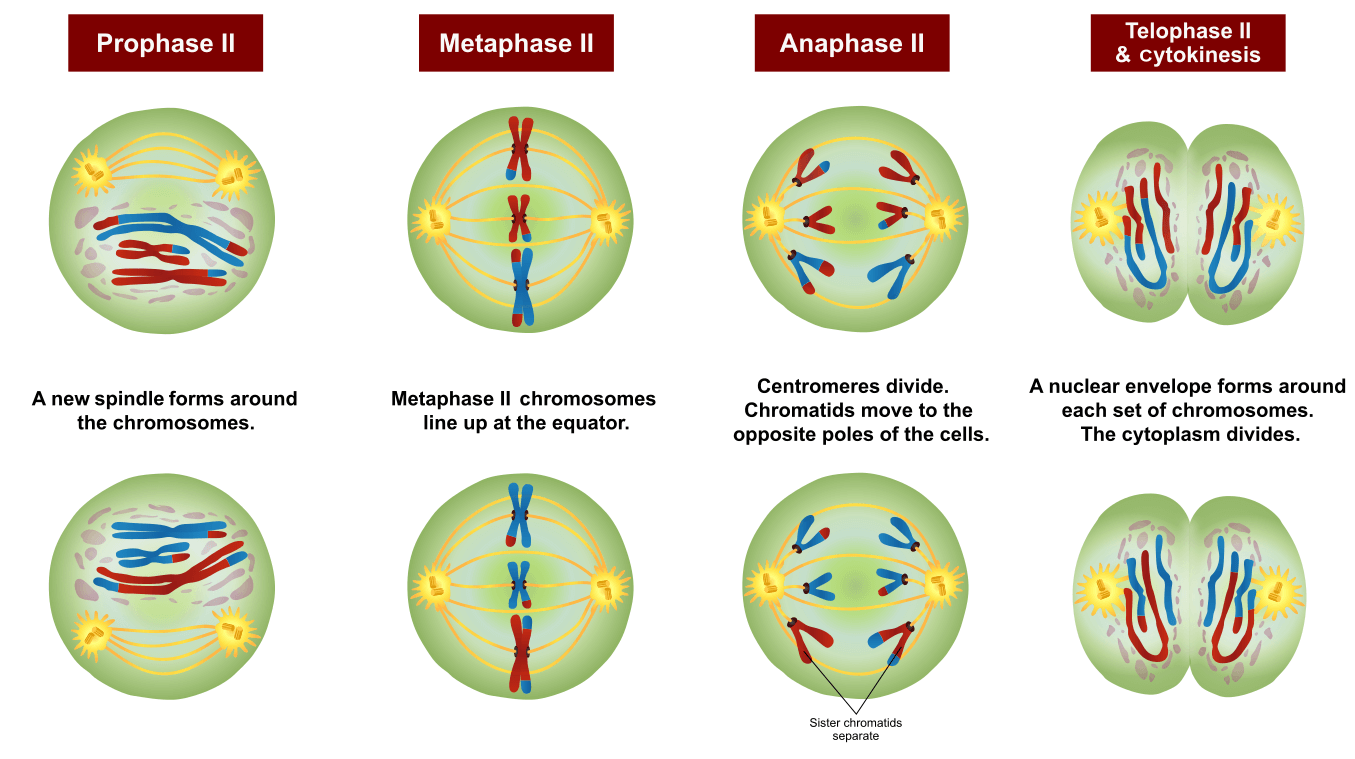
Anaphase II. The sister chromatids are pulled apart by the kinetochore microtubules and move toward opposite poles. Non-kinetochore microtubules elongate the cell. Figure 11.3.1 11.3. 1: Meiosis I vs. Meiosis II: The process of chromosome alignment differs between meiosis I and meiosis II. In prometaphase I, microtubules attach to the fused.
/meiosis-5734a9b55f9b58723d766340.jpg)
Visualizing Meiosis
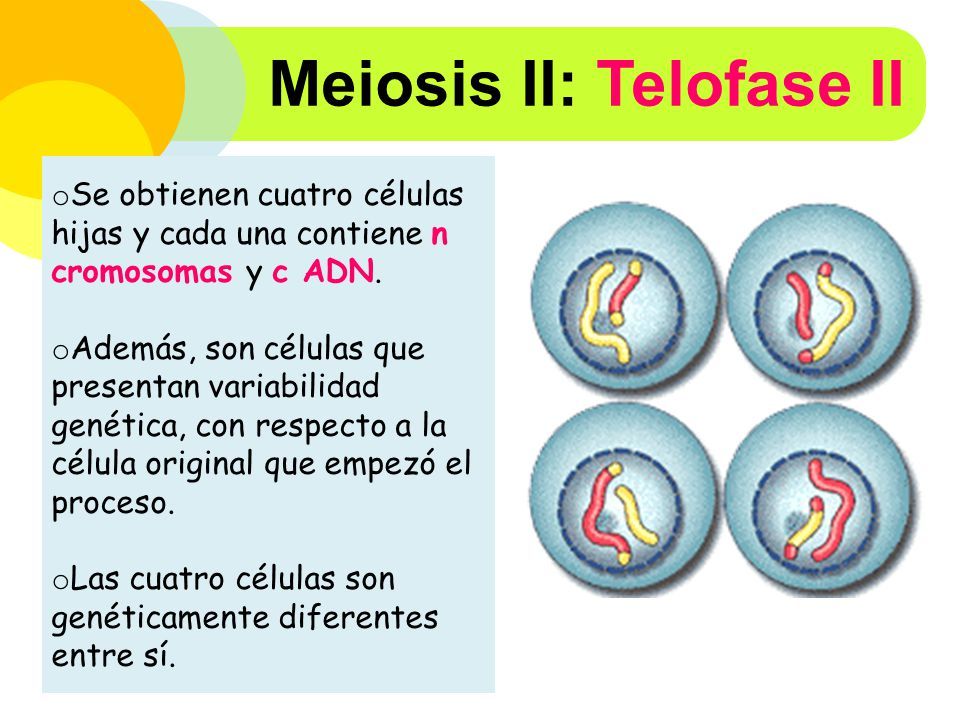
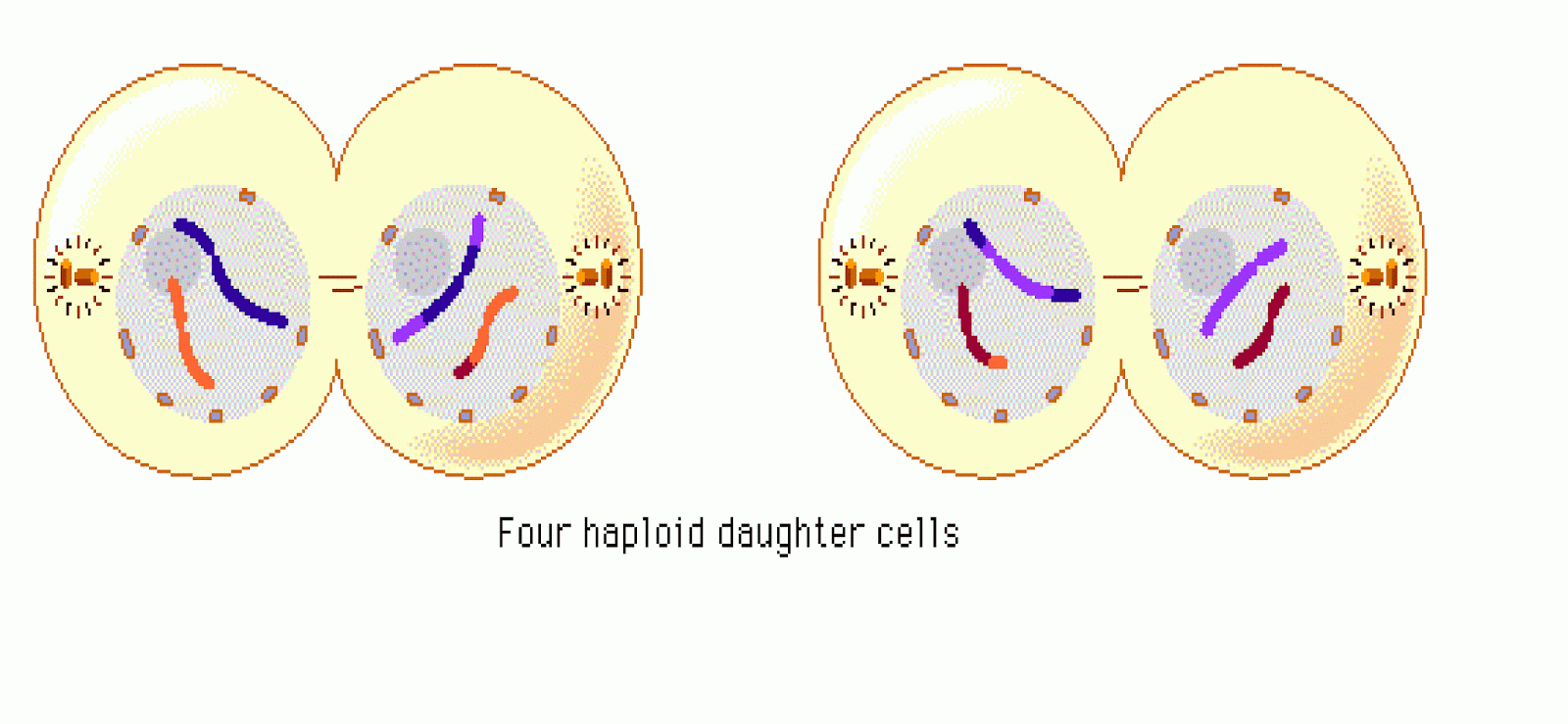
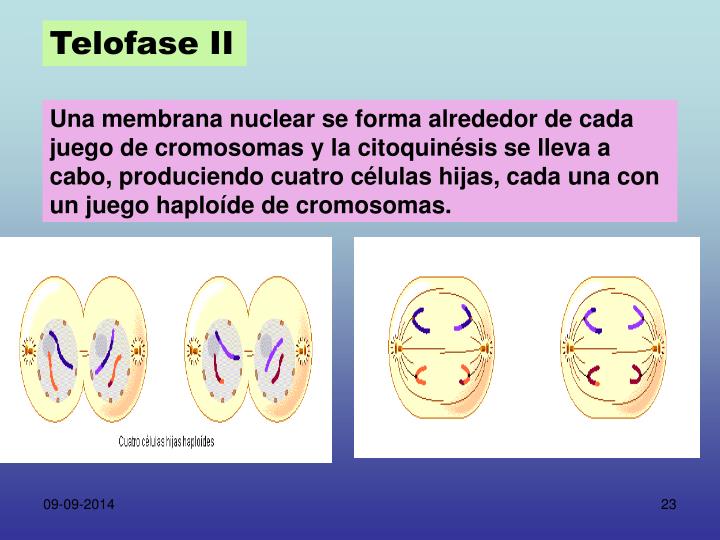
Meiosis: Telophase II. In the final stage of meiosis, telophase II, the nucleus forms around the bundle of chromosomes (Fig. 15). The cell divides. Now four cells exist that originated from one germline cell. Each cell is a gamete with half the number of chromosomes and genes as a somatic cell. Figure 15.
Stages Of Meiosis Simple
To put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a complete diploid set: a new genome.
.PNG)
Variation
meiosis. produces four genetically unique cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as in the parent. mitosis. produces two genetically identical cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as in the parent. Meiosis begins with a diploid cell, which contains two copies of each chromosome, termed homologs.
Qué es la meiosis
Figure 11.2.1 11.2. 1: Meiosis I ensures unique gametes: Random, independent assortment during metaphase I can be demonstrated by considering a cell with a set of two chromosomes (n = 2). In this case, there are two possible arrangements at the equatorial plane in metaphase I. The total possible number of different gametes is 2n, where n equals.
Stages Of Meiosis 2
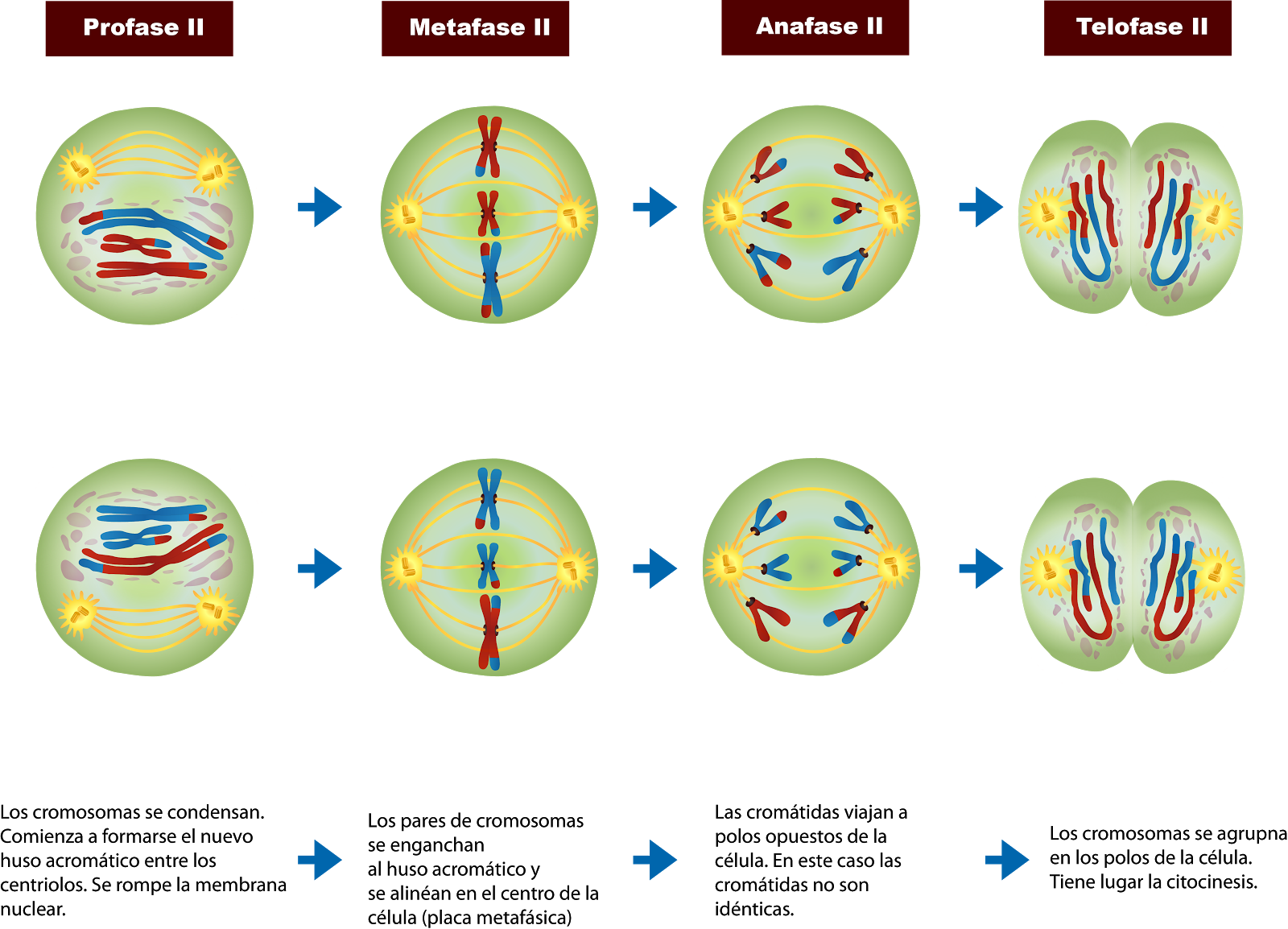
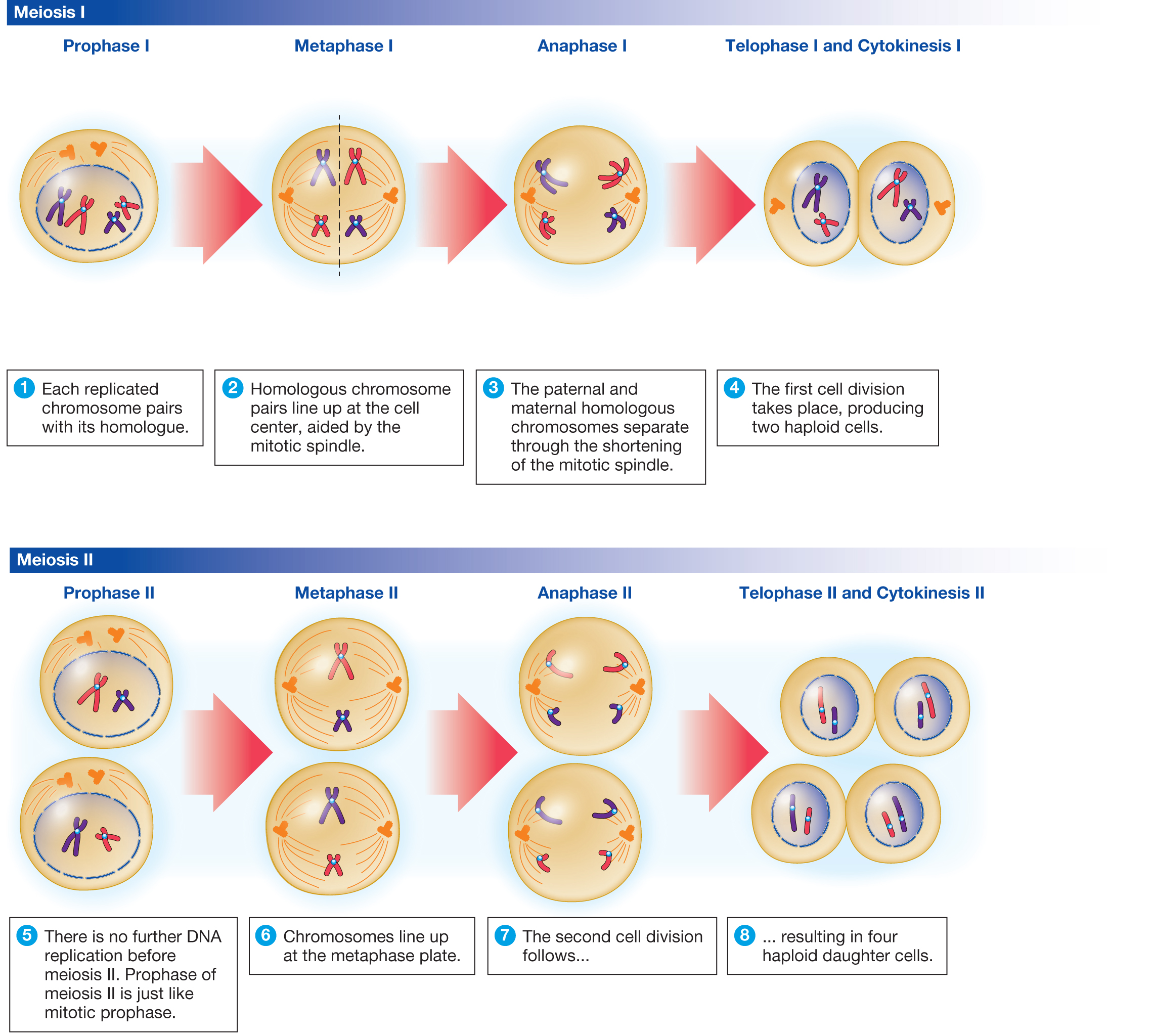
Non-kinetochore microtubules elongate the cell. In meiosis II, the connected sister chromatids remaining in the haploid cells from meiosis I will be split to form four haploid cells. The two cells produced in meiosis I go through the events of meiosis II in synchrony. Overall, meiosis II resembles the mitotic division of a haploid cell.
Meiosis Telophase 2
Meiosis I. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of G 1, S, and G 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The G 1 phase (the "first gap phase") is focused on cell growth. During the S phase—the second phase of interphase—the cell copies or replicates the DNA of the chromosomes.
PPT MEIOSIS PowerPoint Presentation ID4158246
Passing on a complete set of human genes requires one chromosome from each pair to end up in each gamete. There are several key differences between meiosis and mitosis that are summarized in the following table: Table 1. The key events that happen in each of the stages of meiosis are summarized. Mitosis.
Meiosis Stages Simple
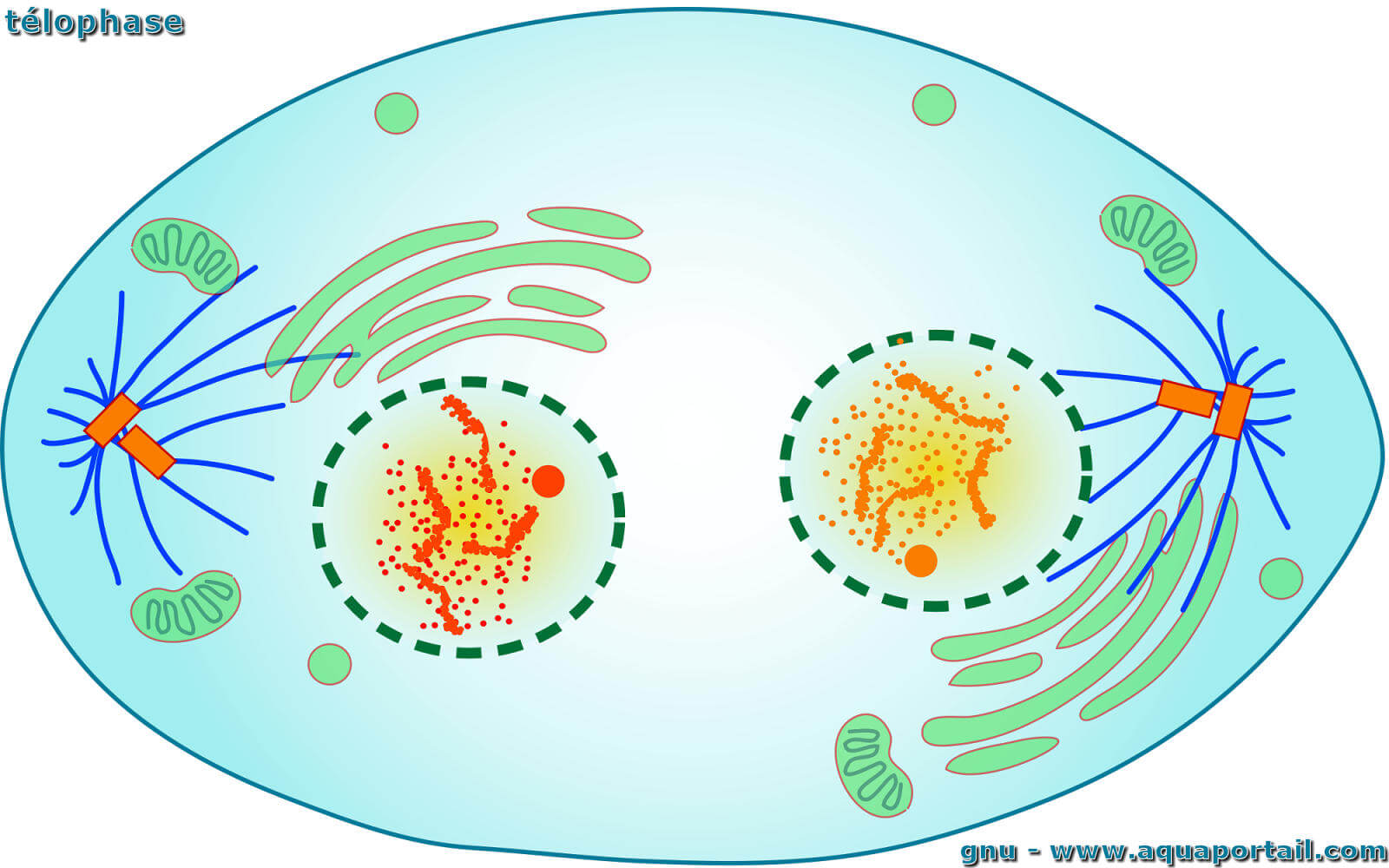
Telophase in Mitosis. Telophase is the final stage of mitosis. The sister chromosomes, once sister chromatids, have now been segregated to the far poles of the cell. The mitotic spindle is no longer necessary because the chromosomes completed their journey. The tubulin dimers fall apart, and much of the microtubule network is disassembled.

Telophase 2 Diagram
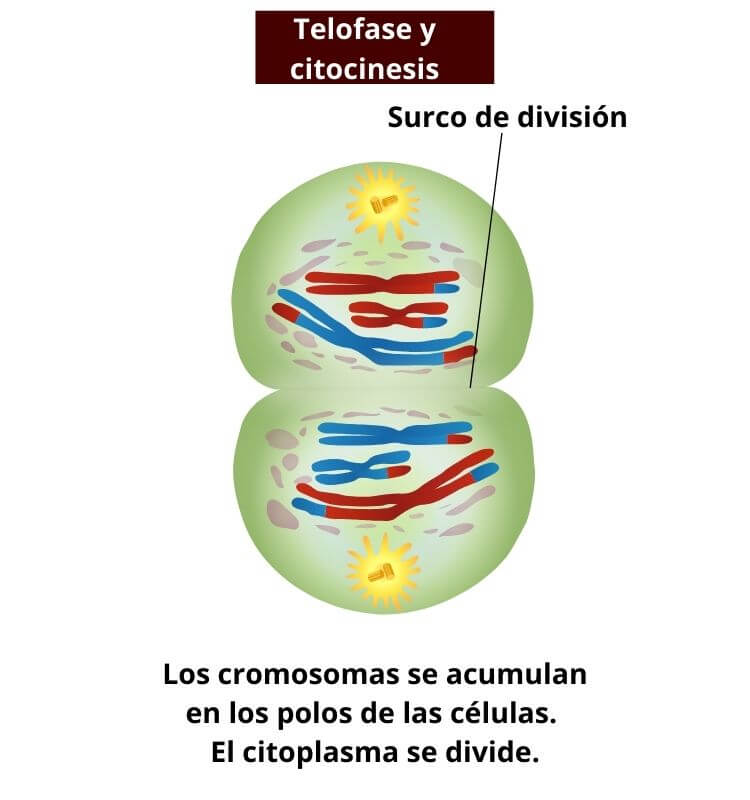
Stages of Meiosis. During telophase II, the fourth step of meiosis II, the chromosomes reach opposite poles, cytokinesis occurs, the two cells produced by meiosis I divide to form four haploid daughter cells, and nuclear envelopes (white in the diagram at right) form. When telophase II is over, the two cells are entirely separated and their.
Télophase définition et explications
Stages of Meiosis II. Prophase II - It immediately sets off after the cytokinesis when the daughter cells are formed. The chromosomes begin to condense accompanied by the dissolution of the nuclear membrane and the disappearance of the Golgi apparatus and ER complex. Metaphase II - The chromosomes are connected to the centriole poles at the.
Meiosis qué es, función, fases y sus características
In meiosis, there are two phases: telophase I and telophase II. This is the separation stage of duplicate genetic materials carried in the cell nucleus of the parent cells. They end up forming two identical daughter cells. Telophase starts after replication when the paired chromosomes are separated and pulled to the cell's opposite poles.

Telophase — Definition & Diagrams Expii
Meiosis is the process in eukaryotic, sexually-reproducing animals that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction. Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such as egg and sperm. The gametes can then meet, during reproduction, and fuse to create a new zygote. Because the number of alleles was reduced during meiosis.
Cell Cycle Mitosis And Meiosis
The body is made up of trillions of somatic cells with the capacity to divide into identical daughter cells facilitating organismal growth, repair, and response to the changing environment. This process is called "mitosis." In the gametes, a different form of cell division occurs called "meiosis." The outcome of meiosis is the creation of daughter cells, either sperm or egg cells.

Meiosis Learning Objectives Learners should be able to
A sex cell (in humans: sperm for males, and eggs for females) Meiosis. A two-step process of cell division that is used to make gametes (sex cells) Crossing over. Process in which homologous chromosomes trade parts. Interphase. Phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows and makes a copy of its DNA. Homologous chromosomes.

Stages Of Meiosis 2
Meiosis I. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated into two cells such that there is one chromosome (consisting of two chromatids) per chromosome pair in each daughter cell, i.e. two chromosomes total. Prophase I. Prior to prophase, chromosomes replicate to form sister chromatids.There are initially four chromatids (c) and two chromosomes (n) for each of the 23 chromosome pairs (4c.